From the ancient Greek "arthrosis" it is a joint disease ("Arth-"-joint, "-isis" -Ida). Sometimes it is also called osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis deforming (from the ancient "Osteone" Greek - Bone).
It will be wrong to call the arthrosis of the disease: this is the name of an entire group of states, which includes many diagnoses.
Any disease of any articulation, regardless of the cause, can be called arthrosis, but this will not give the doctor or patient anything: the word "arthrosis" is not associated with the cause of the disease or treatment, but only with some symptoms.
The word "arthrosis" is very similar to another term - "This is arthritis". Both describe the damage to the joints, often both are associated with pain in the joint, but they have significant differences.

Typically, arthritis is a disease associated with inflammation in the joint: infections, hereditary or autoimmune diseases lead to the beginning of arthritis. Its main manifestations include pain, color change, swelling in the area of inflamed joint.
With arthrosis, the manifestations are less evident and the causes are completely different.
How the joint works (knee and others)
The musculoskeletal system needs a person for active movements in space. The bones are a rigid frame, the muscles - their driving force and the joints - the place of the mobile connection of the bones.
In the structure of the joint there are always two ends of the nearby bones that can move compared to the other with the help of the muscles and a small gap between them. This joint gap is filled with a synovial fluid of special lubricant. It is necessary for the nutrition of the cartilage: there are no vases inside, so it takes all the nutrients from the synovia.
The joint end of each bone is covered with cartilage to protect bone tissue from friction. Cartilage also helps to "extinct" the vibration and an acute mechanical load: for example, the knee and the joints of the foot during the walk take most of the energy from the blow of the foot to the ground.
The restoration of this cartilage is a long and complex process that does not always end successfully.
All joints are limited by a capsule - a film that contains the joint fluid, does not allow it to spread. Almost all joints are supported by ligaments that do not allow the close bones to move too much and in the wrong direction.
Because and how arthrosis develops
There are many reasons for the onset of osteoarthritis, in some cases it is a combination of factors, and sometimes it is impossible to establish the cause.
There are three main causes and more than a dozen further. The most popular:
- joint injury;
- congenital joint anomalies (dysplasia);
- The consequence of the inflammation (arthritis) of any reason;
- age (usually more than 50 years);
- Violation of metabolism (trace elements), obesity;
- Excessive load on the joint.
The development of osteoarthritis is divided into three phases:
- Initial. There are no obvious signs, it is difficult to find it. The composition of the synovial fluid is changing, its function worsens.
- Pain. Structural complaints and changes appear in the form of bone flows - osteophytes.
- Severe arthrosis. A significant reduction in the function of the joint is added: the movements are reduced or completely disappeared; The joint is deformed and the appearance of the limb changes.
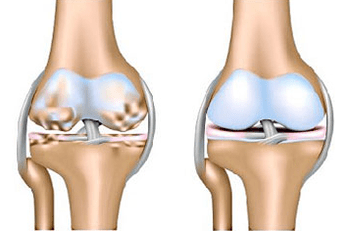
First of all, the structure of the cartilage is disturbed: it is thickened due to a change in the composition of the synovia or for another reason. The swelling of the cartilage tissue worsens its diet, then over time the cartilage begins to become thinner.
So, in the most loaded parts of the joint, the cartilage almost disappears or becomes too tight. In return, the growth of the bone begins: the appearance of osteophytes (bone "peaks).
At the end of the disease, the growth of the bone is thus pronounced that limits the movement to anchynosis - the complete immobility of the joint.
Symptoms of arthrosis
Initial manifestations: periodic pain after a significant physical activity. So the morning rigidity joins: after waking up for several minutes (up to 30), the joint seems to be connected by an elastic bandage: the movements are possible, but difficult.
Subsequent symptoms:
- Palpation pain in the joint;
- thickening of the bone in the joint;
- restriction of the movement;
- increase in pain during the least significant physical activity;
- Deformation of the limb.
Very often, arthrosis is a disease of great joints of the legs (knee, hip) and hands (shoulder). The joints of the foot are less common.
The degenerative processes in the joint can still manifest themselves in the form of unusual sounds during the movement: crunch, cracking, shock.
Diagnostics
As in the case of any other disease, it begins with the collection of an anamnesis: the history of the disease.
It is particularly important for the doctor to find out if there was the presence of risk factors (injuries, arthritis, congenital defects, chronic diseases).
After talking and inspecting the joint, further methods will be needed: test and instrumental examination.
The main study in the diagnosis of arthrosis is radiography.
The image will clearly see the main changes in the articulation: reduction of the joint gap, bone growth, deformation. In the initial stages, small osteophytes can be seen along the edge of the joint and in the illegal growth growth of the bone along the entire joint gap will be considerably.
The examination of ultrasound (ultrasound) is an additional method that will help determine the thickness of the cartilage in the early stages of clay. Artroscopy is less common: a surgeon inserts a small camera directly into the joint space and obtains the image of the cartilage.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
It is impossible to completely treat arthrosis and return the joint to the original state. The correct combination of different methods will slow down only the development of osteoarthritis, but "to return the former young man" will not work.
The main duties of the deformo -art -arthrosis treatment of the knee or hip joint:
- moderate physical activity (race, walking, sitting position);
- Special exercises, exercise therapy (physiotherapy exercises);
- diet;
- pharmacological treatment;
- surgical treatment.
With the arthrosis of the shoulder joint or other location, the principles do not change, with the exception of the correction of the load on the specific articulation.
Physical activity and exercises are selected in any case with an orthopedist-traumatologist by a doctor. The diet usually includes the enrichment of the diet with unsaturated fatty acids, a variety of proteins, moderately limits carbohydrates (especially simple ones, are "fast").
The refusal of bad habits (smoke, taking alcohol in any quantity) significantly slows down the development of osteoarthritis. The diet also depends on the cause of the disease, on chronic diseases. Food supplements should not be taken.
Drug Therapy - painkillers. Of NSAIDs -anti -anti -inflammatory drugs are used more often. The choice of adaptation depends on the presence of chronic diseases and the planned duration of the administration. Less commonly used are corticosseeroids (glucocorticoids, steroid drugs).
Very often, doctors prescribe Condroproproprotectors - drugs that contain some of the important molecules for cartilage. In the vast majority of cases, these drugs have no effect on the joint, in particular forms and ointments.
It is extremely rare that these drugs can really be necessary and give a real effect: when examining the intra -articular fluid, you can verify the quantity and with a lack of injected directly into the joint (intra -articular injection).
Conclusions
Arthosis is a degenerative joint disease associated with mechanical damage to cartilage and the growth of bone tissue. Usually it develops in people over the age of 50, after joint lesions or a long -term excess load.
It manifests itself from pain after loading, morning rigidity and creaking.