Osteochondrosis is a widespread disease of the intervertebral discs, which affects people of various age groups.Today it is diagnosed in over 40% of young people under 35 and among older people it affects 9 out of 10 people. It has different stages of development and the earlier the pathology is detected, the simpler and more effective the treatment and the lower the risk of developing dangerous complications.
What is osteochondrosis
Intervertebral discs are located between the vertebral bodies and are a kind of shock absorbers that absorb stress when walking or performing other physical activities.They have different sizes depending on their position: in the cervical region the discs are the smallest, while in the lumbar spine they are the largest.
They are all built the same way.In the center is the nucleus pulposus, which is the main component of the disc and has high elasticity.It is surrounded by a fibrous membrane and endplates.
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in which a change in the shape and size of the intervertebral discs occurs due to their abrasion and the conditions are created for the formation of hernias, deformation of the vertebral bodies, spondylosis and other disorders.
The thinning of the discs is a consequence of malnutrition of the cartilaginous tissue, which leads to a gradual decrease in its elasticity and increased fragility.
As a result, the discs change position, their height decreases, and microcracks form on their fibrous membrane.This creates serious conditions for the formation of intervertebral hernias, pinching of the spinal roots or blood vessels.
The slightest changes in the condition of the disks lead to the interruption of their functions.This is accompanied by pain of varying degrees of intensity.At the same time, prerequisites for the development of diseases of internal organs are created, since the quality of their activity directly depends on the condition of the spine and the conductivity of bioelectric impulses along the nerves.
It can affect one or more intervertebral discs anywhere in the spine.Therefore, osteochondrosis is diagnosed:
- cervical spine;
- thoracic spine;
- lumbar spine.
In particularly severe cases, the pathological process involves most of the intervertebral discs of the spine, accompanied by discomfort throughout the back and an almost complete loss of performance.But most often osteochondrosis affects the lumbar spine, as it bears the greatest load, as well as the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine due to their high mobility.
Development
During osteochondrosis, approximately 4 stages can be distinguished:
- A decrease in the level of hydration of the disc, which leads to its dehydration and the formation of microcracks.Often at this stage there are still no manifestations of the incipient disease.
- A decrease in the height of the disc, which leads to the appearance of the first symptoms of the pathology.At this stage, a decrease in the distance between individual segments is observed, which leads to a decrease in the tone of the spinal ligaments and creates the possibility of displacement of the vertebrae from their natural positions, that is, the development of spondylolisthesis.In such situations, a wave-like course of the disease is most often observed.It can distinguish between periods of exacerbation, accompanied by acute pain, and periods of remission, in which no discomfort is felt or aching pain is felt.
- Deformation of the affected intervertebral disc with formation of protrusion or prolapse.Sometimes there is involvement of the joints in the pathological process, which is manifested by the development of arthrosis or vertebral subluxations.At this stage, the immune system reacts to the processes occurring in the spine by developing aseptic inflammation with swelling of the tissues surrounding the affected spinal-motor segment.In this case, pain occurs regularly, reflex muscle spasms and limitations in mobility may be observed.In rare cases, signs of neurological deficit (radicular syndrome) already develop due to crushing of nerve fibers by the resulting protrusions of the intervertebral discs.
- Development of complications.Since the human body has extensive compensatory capabilities, when the intervertebral disc loses the ability to perform its functions, the process of osteosynthesis is activated to secure the vertebrae in a stable position.This leads to the formation of bony protuberances - osteophytes - at the edges of the vertebral bodies of the affected spinal motion segment.As a result, due to them, two or more vertebrae firmly fuse together, forming a single conglomerate, that is, spondylosis develops.This always leads to compression of the nerves and the development of acute neurological symptoms in the form of paresis, paralysis and serious disturbances in the functioning of the corresponding internal organs.
Reasons
Today there are many theories of the development of osteochondrosis, including vascular, mechanical, hereditary, hormonal, infectious-allergic and others.But none of them is able to fully explain the mechanism of development of changes in the tissues of the intervertebral discs.Therefore, most likely, they complement each other.
Therefore, a huge number of very different factors can lead to the development of osteochondrosis.Among these, the most significant are:
- genetic predisposition;
- regular performance of heavy physical work;
- maintain a sedentary lifestyle;
- the presence of scoliosis or other spinal deformities;
- suffers from back injuries;
- unbalanced diet, vitamin deficiency;
- infectious diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- congenital anomalies of the spinal column (Kimerli anomaly, Chiari anomaly, craniovertebral anomalies, sacralization, lumbarization);
- overweight;
- strong regular stress.
It is believed that the most significant influence on the condition of the intervertebral discs is the constant overload of a certain movement segment of the spine.This may mean not only performing hard and monotonous physical work, but also constant stooping or the habit of sitting for long periods of time.In such situations, additional stress is placed on the discs, muscles and ligaments, and other factors only aggravate the situation.
In general, osteochondrosis can be called an almost natural age-related disease, which is an inevitable price to pay for walking upright.
Symptoms
The first sign of the development of the disease is the appearance of a creaking sound in the part of the spine where the onset of degenerative-dystrophic changes is observed.It is a consequence of the onset of disorders in the nutrition of the disc and the progression of its dehydration.At this stage, patients almost never seek medical care.Therefore, the daily routine, eating habits and other factors remain the same, which contributes to the worsening of the situation and the transition of the disease to the second stage.
As a result, typical symptoms of osteochondrosis begin to appear:
- severe muscle tension in the affected area on only one or both sides of the spine;
- sharp, aching pains that intensify with every movement and gain intensity over time, becoming unbearable;
- numbness in the arms or legs;
- weakness;
- stiffness of movements, unauthorized limitation of mobility;
- decrease in muscle tone up to complete atrophy;
- bad posture;
- changes in blood pressure.
As the pathology progresses, the signs of osteochondrosis worsen.80% of patients feel a dull pain in the area of the affected spinal motion segment, which is also characteristic of myositis.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
When the cervical spine is affected, the pain tends to radiate to the shoulder girdle, arms and other manifestations of neurological disorders occur.Patients hold their head in the least painful position and, if necessary, turn their whole body.
In addition, pathologies of the organs innervated by the spinal cord region of the cervical spine may develop:
- tinnitus and diseases of the ENT organs;
- dizziness;
- blurred vision;
- migraine;
- increased levels of irritability and anxiety;
- sleep problems;
- increased risk of allergic reactions;
- decreased levels of thyroid hormones.
With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, vertebral artery syndrome and vegetative-vascular dystonia are also often diagnosed.
Infection of the cervical spine with osteochondrosis, especially if complicated by intervertebral protrusions and hernias, can lead to pinching of blood vessels.This is fraught with reduced blood supply to the brain, which can be accompanied by attacks of dizziness, loss of consciousness and even a stroke.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, which is diagnosed quite rarely, pain occurs in the spine at the level of the shoulder blades and can intensify even when taking deep breaths.They are often felt behind the breastbone and can be confused with heart disease.
When the spinal roots are pinched, the risk of diseases of internal organs increases, in particular:
- bronchi and lungs (asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy);
- gallbladder and its duct, liver (cholecystitis, jaundice, disorders of fat absorption);
- pancreas and duodenum (digestive disorders, pain in the left hypochondrium);
- adrenal glands, which affect the overall strength of the immune system and can cause the development of allergies;
- kidneys (urinary disorders, chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.);
- pelvic organs (digestive disorders, gynecological, urological diseases, infertility).
Fact: Damage to the intervertebral disc of the 7th thoracic vertebra caused by osteochondrosis can lead to the development of diabetes mellitus.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine
With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, low back pain, called lumbago, is observed.This is accompanied by a burning, unbearable pain that occurs suddenly.Patients often also have difficulty sitting, standing, and walking, which may indicate the development of radicular syndrome.In such situations, it is easy to notice how they sit down and stand up slowly, trying as much as possible to avoid tilting their torso.
If complications occur, the main danger is pinching the nerves of the cauda equina, as this can lead to impaired control over the processes of emptying the intestines and bladder, as well as paralysis of the legs.Even in these cases the following can develop:
- appendicitis;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- lower abdominal pain;
- bladder dysfunction;
- impotence;
- pain in the knees, feet, hips, or groin area;
- swelling of the legs.
Complications
Osteochondrosis is a possible cause of a large number of different diseases.Very often, if untreated, it leads to the formation of intervertebral protrusion and hernia.This in turn can cause:
- discogenic myelopathy, ending in paresis, muscle atrophy, changes in tendon reflexes, loss of control over urination and defecation, and even paralysis of the limbs;
- radiculopathy;
- scoliotic deformity or other spinal deformity;
- spinal cord infarction due to compression of the artery supplying it;
- stroke due to compression of the occipital artery.
Diagnostics
The appearance of pain in the back and neck should be a reason to contact a neurologist or vertebrologist.The earlier osteochondrosis is diagnosed, the simpler and more effective the treatment will be.
To diagnose the disease, the doctor interviews and examines the patient.Based on their results it is already possible to hypothesize the presence of degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs.But for the final diagnosis, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed, including:
- MRI;
- CT;
- x-ray in two projections.
MRI provides the most complete information on the condition of the intervertebral discs.The procedure is carried out mainly in closed-type devices with a power of 1.5 T. With its help, it is possible to differentiate osteochondrosis from tuberculous spondylitis, osteomyelitis, infectious diseases, etc.
CT scans and x-rays provide information about the bony structures of the spine.Thanks to them it is possible to detect displacements of the vertebral bodies, presence of osteophytes and other disorders.
Additionally, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound with Dopplerography of the neck vessels;
- electromyography;
- laboratory research.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Therapy is developed individually for each patient.In this case it is necessary to take into account the severity of the degenerative-dystrophic processes, the presence of complications, the nature of the patient's work activity and a series of other factors.
All patients should be prescribed a set of measures, since it is impossible to eliminate pathological changes in the intervertebral discs only with the help of drugs.Components of conservative therapy for osteochondrosis may include:
- drug therapy;
- osteopathy;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy (phonophoresis, ozone therapy, carboxytherapy, pressotherapy, RF currents);
- individual sessions with a rehabilitator.
All patients diagnosed with intervertebral disc dystrophy are advised to reconsider their lifestyle.It is imperative to set aside time for moderate physical activity, especially for representatives of sedentary professions, or, conversely, think about the possibility of changing professions for people forced to lift heavy objects every day.
But in the acute period complete rest is recommended.It is ensured not only by maintaining bed rest, but also by wearing orthopedic bandages: in case of damage to the cervical spine, a Shants collar is used;in case of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region it is recommended to wear a corset.
In the early stages of the development of the disease, it is often enough to make changes to your lifestyle, engage in physical therapy and visit a chiropractor.In more advanced cases, drug therapy and physiotherapy are necessarily prescribed.
Never resort to self-medication with dubious means, self-prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as dubious "healers" placed on the Internet - you can lose not only time, money, but also remnants of your health.
Drug therapy
For osteochondrosis, a complex of drugs is prescribed to reduce pain, eliminate inflammation and reflex muscle spasms, improve nerve conduction and activate the tissue regeneration processes of the intervertebral discs.
Therefore, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs – help reduce pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- corticosteroids – show powerful anti-inflammatory properties;
- muscle relaxants – eliminate muscle spasms, helping to reduce back pain;
- B vitamins – improve the functioning of the nervous system in general and in particular the conduction of nerve impulses along individual nerves;
- vitamin D is a remedy responsible for the condition of bone tissue, as well as higher brain functions, such as memory, attention, speech;
- chondroprotectors – nourish the intervertebral discs with the compounds necessary for the construction of new fibers of the nucleus pulposus;
- psychotropic drugs – increase the effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants;
- vascular drugs: improve blood circulation in the tissues surrounding the spine, ensuring a more active supply of nutrients and oxygen to the intervertebral discs;
- Anticonvulsants – used in rare cases to relieve very severe spasms.
In case of very severe pain, which most often indicates complications, patients can undergo back blocks, which provide an immediate effect.Corticosteroid hormones are sometimes added to the solution to perform the blockade.This also leads to a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
Blocks are performed under conditions of absolute sterility, which can only be obtained in specialized medical institutions.At the same time, they require special knowledge and skills, so only a highly qualified healthcare worker can competently cope with the task.Otherwise there is a high risk of infection or damage to the nerve fiber, which will lead to the development of serious complications.
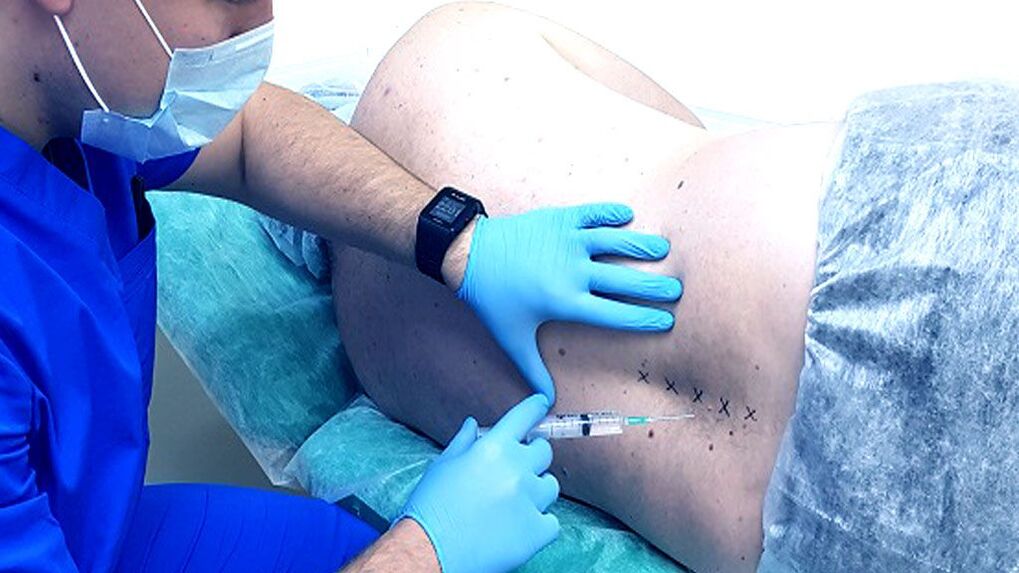
During the block, injections are usually given to both sides of the spine in the area where the nerves causing pain occur.There are several techniques for performing them, among which the specific one is selected individually by the doctor.
But it is advisable to carry out blocks no more than 4 times a year.Since with osteochondrosis acute and aching pain attacks occur much more often, it is worth first of all directing efforts to eliminate the causes of their occurrence, i.e.the degenerative-dystrophic process in the joint itself.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy sessions are prescribed outside the period of exacerbation of osteochondrosis.They play one of the main roles in the treatment of the disease, since the competent use of manual techniques on the spine and surrounding tissues helps not only to stop the progression of the pathological process in the intervertebral discs, but also to create the most favorable conditions for their restoration.
Furthermore, some techniques can also have a positive effect on the functioning of internal organs.For example, one of the methods is designed to eliminate pressure on the spinal roots, blood vessels and spinal membranes, normalizing the position of each vertebra, thereby restoring the normal connection of the organ with the nervous system.This allows you to eliminate the hidden causes of the development of the above diseases of the heart, bronchi, lungs, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and reproductive system and leads to complete recovery.
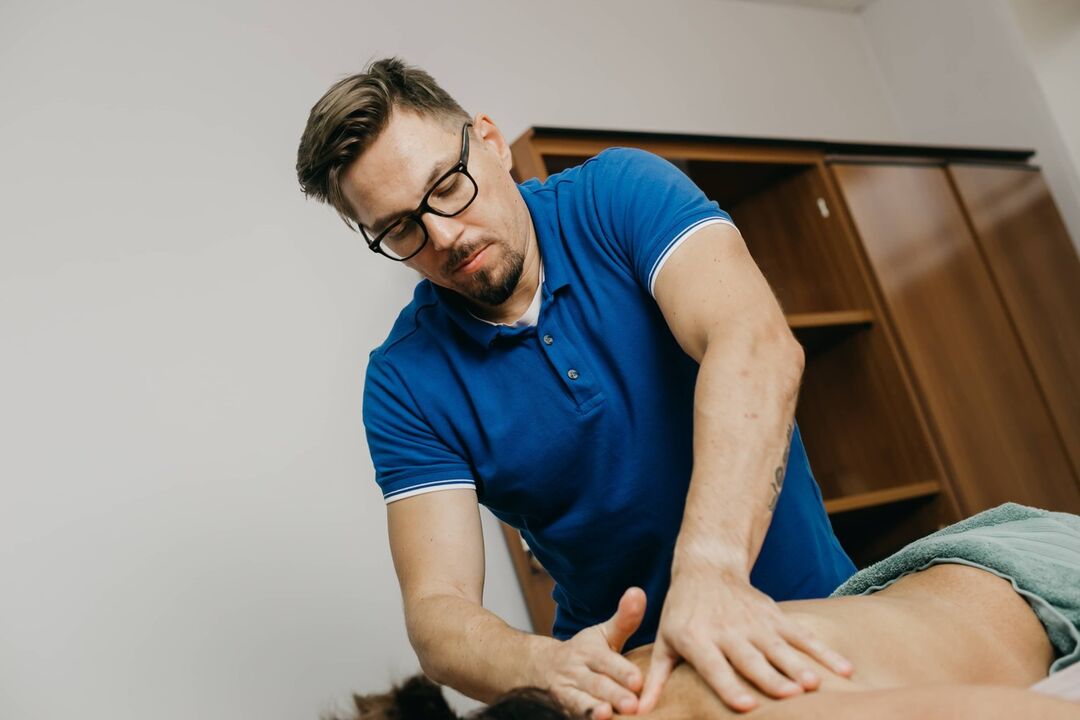

Thanks to the precise effect of the jewels on the spine, not only is blood circulation activated and the metabolism accelerates, as with a classic therapeutic massage, but natural self-healing mechanisms are also initiated.Elimination of curvatures of the spine, incorrect position of the vertebrae and other pathological changes in the spine through manual therapy can further strengthen the immune system, improve overall well-being and significantly improve the quality of life.
Positive changes can be noticed after the first session, and in the future their severity will only increase.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures increase the effectiveness of all other methods of treating osteochondrosis and help reduce pain.Most often used:
- electrophoresis - the use of electric current to ensure the penetration of anesthetics, anti-inflammatory and other agents directly into the site of inflammation, allowing you to quickly achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect;
- Ultrasound therapy: the effect of ultrasound provides an analgesic effect, increases the intensity of metabolic processes in the area of influence and creates prerequisites for high-quality restoration of thinned intervertebral discs;
- detensor therapy – involves stretching and massaging the spine on a special ribbed mattress, which activates blood circulation and increases muscle tone;
- traction therapy or spinal traction – is performed using special devices that create a tensile load on the spine, as a result of which the distance between the vertebrae increases and the pressure on the worn intervertebral disc decreases sharply, allowing it to recover more actively.
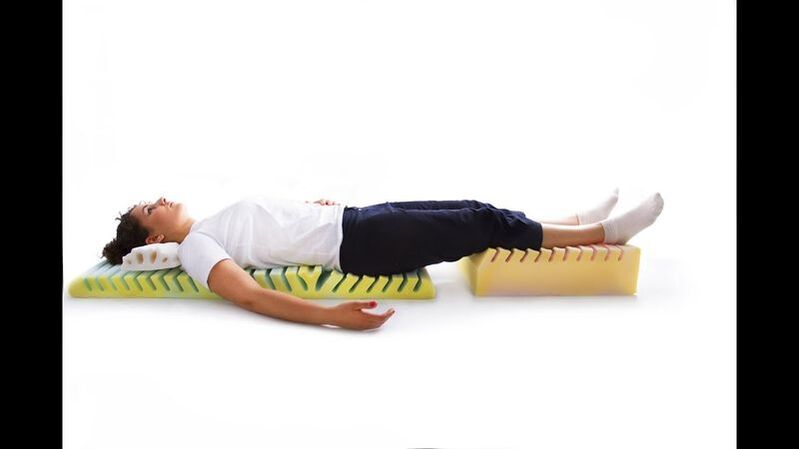

All procedures are prescribed in cycles of 10-15 sessions.When choosing them, they take into account not only the condition of the intervertebral discs, but also the presence of concomitant diseases, since in some of them some physical effects are contraindicated.
Physical therapy
Therapeutic exercises for osteochondrosis play a significant role, since correctly selected exercises for damage to different parts of the spine can help to form a strong muscle corset and at the same time eliminate increased muscle tone.This will provide good support to the spine and stop the progression of the degenerative process in the intervertebral discs.In addition, physical therapy helps to activate blood circulation and increase the intensity of metabolic processes.
The development of a physical therapy program is the responsibility of the rehabilitation doctor.Based on the severity of the spinal injury, the characteristics of the patient's physical development, his age and other factors, he will create an optimal set of exercises, the implementation of which will create an optimal load on the muscles and spine.
The first lessons should be conducted under the supervision of a doctor.Once the patient learns to perform each exercise correctly, he or she can continue practicing them at home.It is important to avoid sudden movements.All exercises are performed slowly and smoothly daily, and the load is increased gradually.But the onset of pain during exercise is a good reason to refuse to perform the exercise that provoked it.

Prevention
It is much easier to prevent the development of a disease than to deal with its consequences later.Since osteochondrosis can occur in everyone sooner or later, it is necessary to think about possible risks as soon as possible and make every effort to prevent it.Therefore, each person should adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid physical inactivity, exercise regularly, swim and, during sedentary work, take regular breaks to warm up;
- pay attention to your posture when walking or sitting;
- purchase a high-quality orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- observe the correct technique for weight lifting: with a straight back and bent knees;
- change casual shoes for more comfortable ones and leave elegant shoes for special occasions;
- eat well so that the body does not suffer nutritional deficiencies and the weight remains within normal limits.
There is only one way to avoid the appearance and manifestation of symptoms of osteochondrosis: start taking care of yourself and your health.Since osteochondrosis is not just a disease, but a complex of tonic-muscular and neurodystrophic changes, which are the body's response to physical inactivity, chronic static tension of the spinal muscles, environmental situation and chronic neurosis, especially common among city dwellers, swimming in the pool and stretching programs, including yoga.
Therefore, osteochondrosis is a very common disease, but with careful attention to your health, you can effectively fight it at any age.But ignoring the problem will not lead to anything good and will sooner or later force the patient to lie down on the operating table.